Sinuses
 Sinus Pressure
Sinus Pressure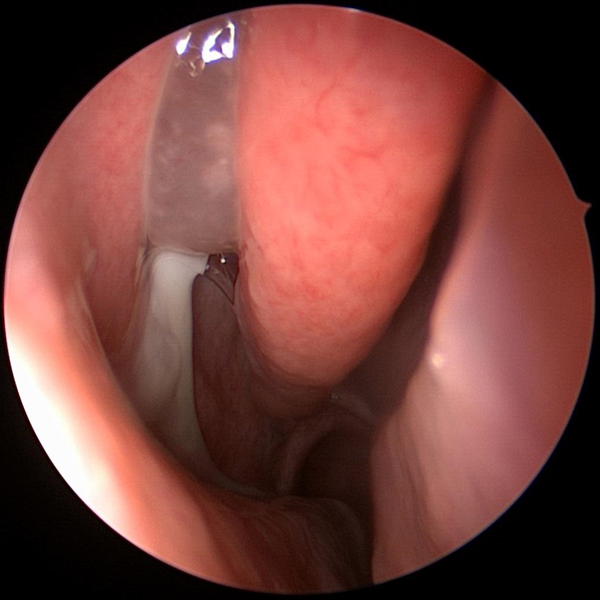 Sinus Headache
Sinus Headache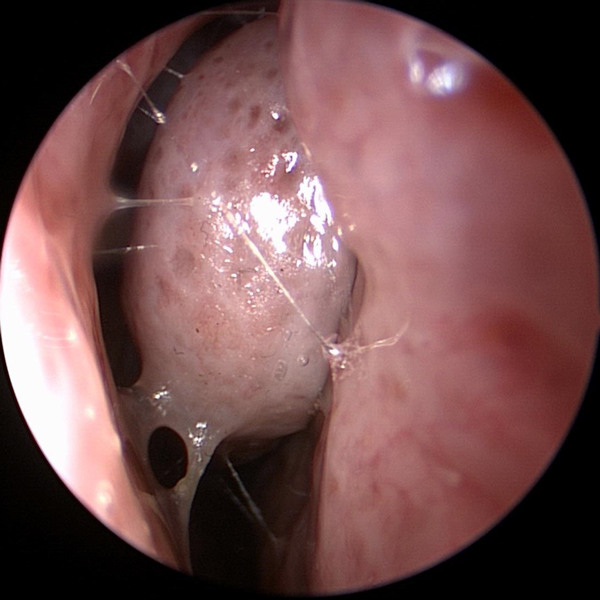 Recurrent Sinusitis
Recurrent Sinusitis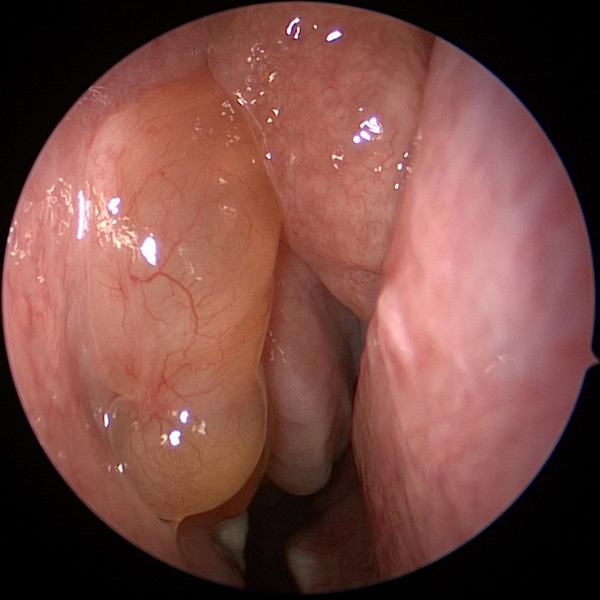 Sinus Polyps
Sinus Polyps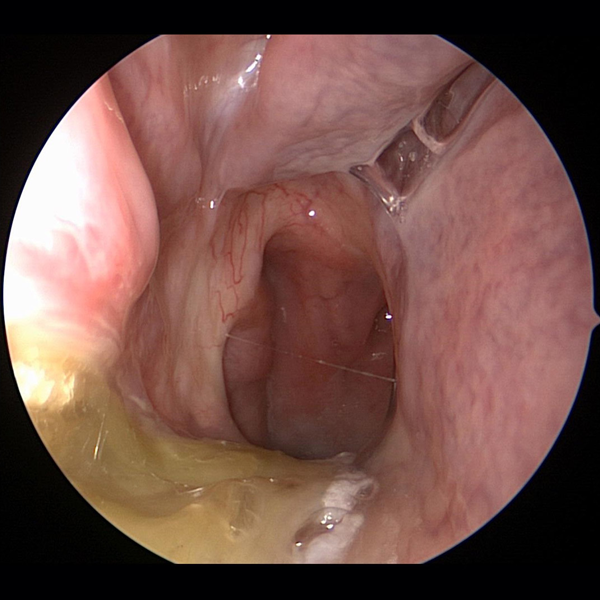 Post Nasal Drip
Post Nasal Drip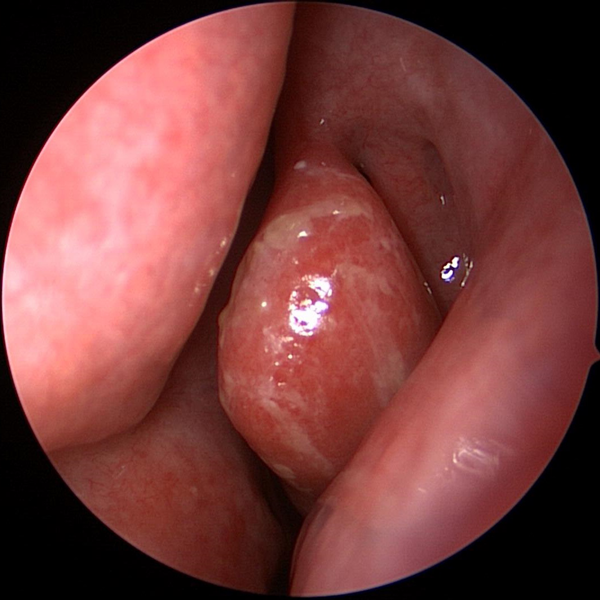 Sinus Problems
Sinus Problems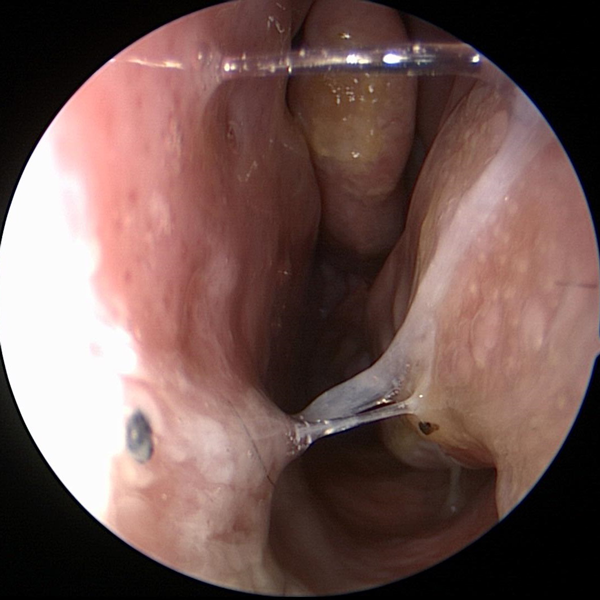 Sinus Allergies
Sinus Allergies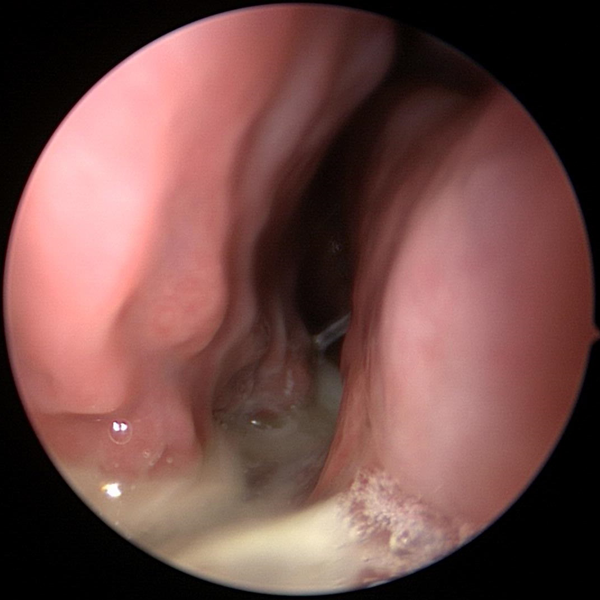 Chronic Sinusitis
Chronic SinusitisNose
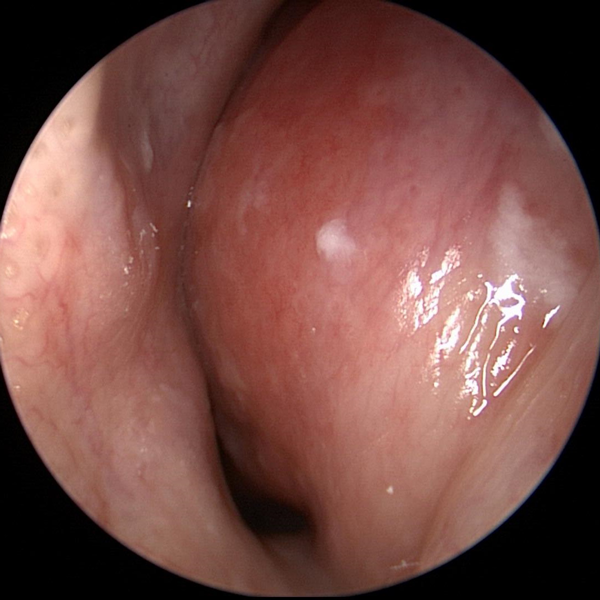 Nasal Obstruction
Nasal Obstruction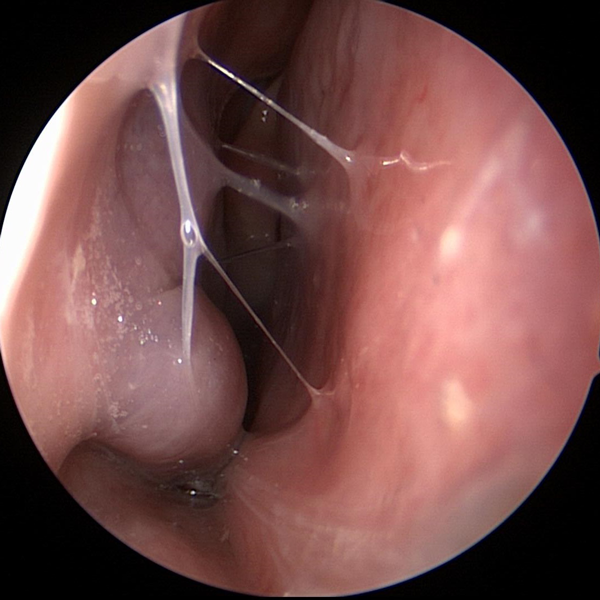 Nasal Congestion
Nasal Congestion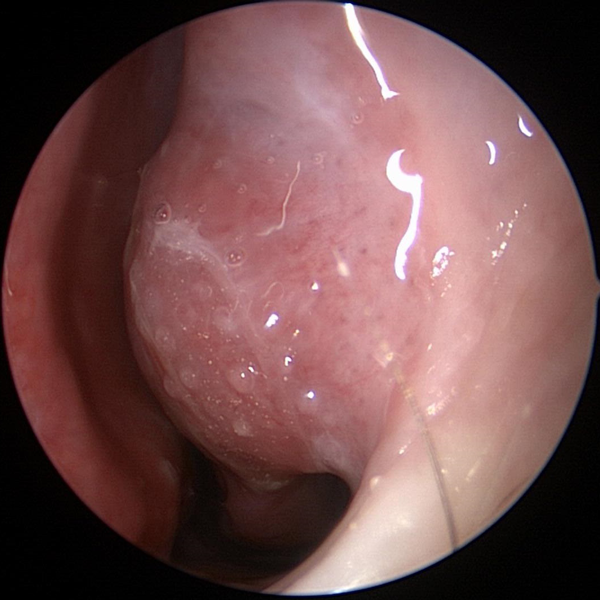 Nasal Allergies
Nasal Allergies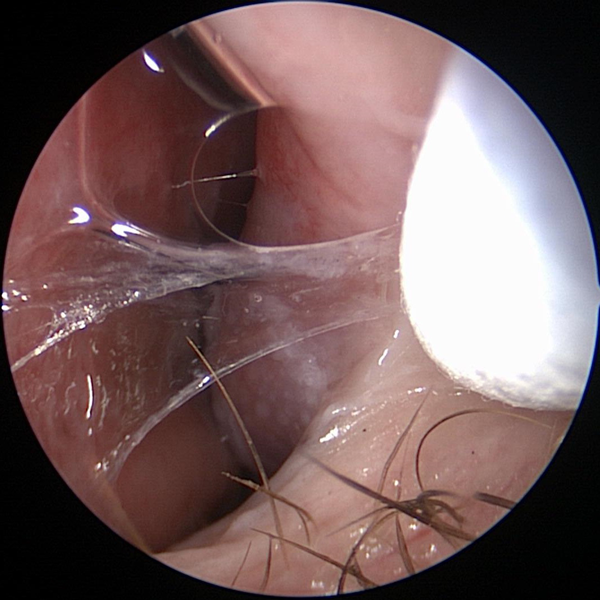 Runny Nose
Runny Nose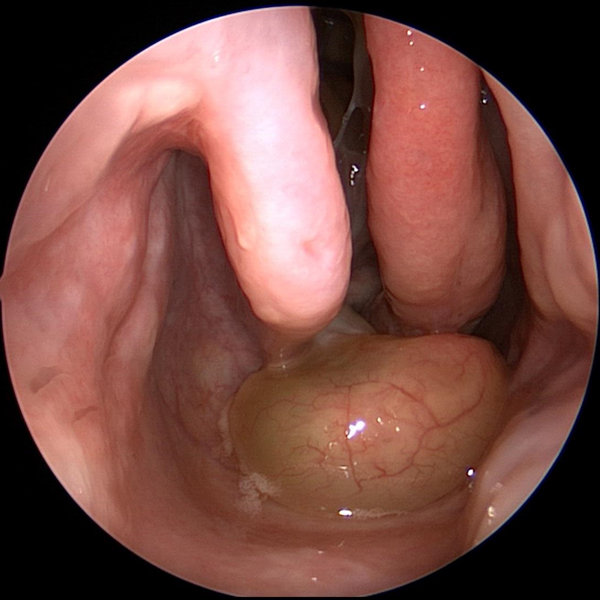 Nasal Polyps
Nasal Polyps Nose Bleed
Nose Bleed Nose Injury
Nose Injury Broken Nose
Broken Nose Deviated Septum
Deviated Septum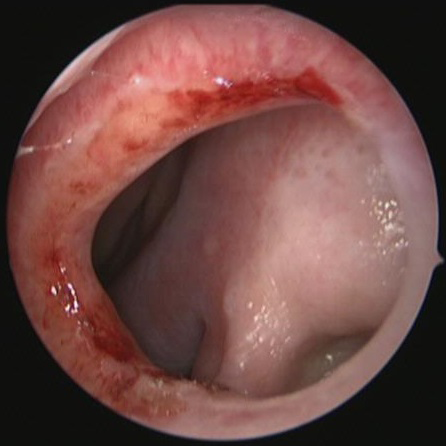 Nasal Septal Perforation
Nasal Septal Perforation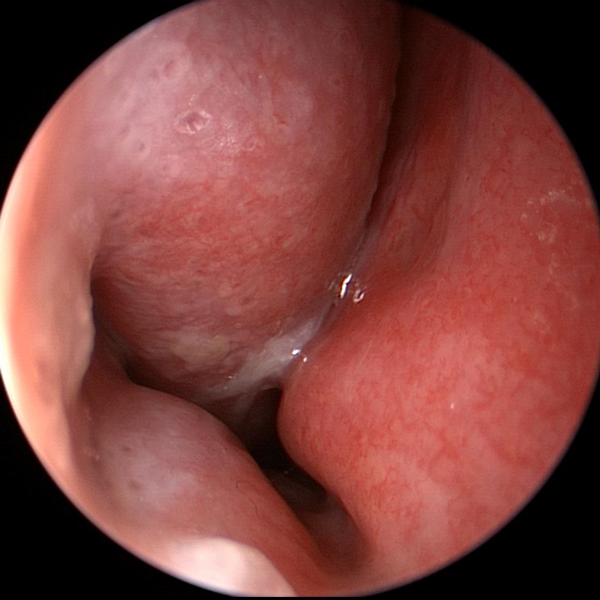 Trouble Breathing Through Nose
Trouble Breathing Through NoseEndoscopic Sinus Surgery
Endoscopic sinus surgery is done entirely through the nose with no need for incisions. Endoscopes (tiny cameras) and special instruments are used to remove tissue that is obstructing the nasal sinuses. This surgery is done to treat conditions like chronic sinusitis and polyps.
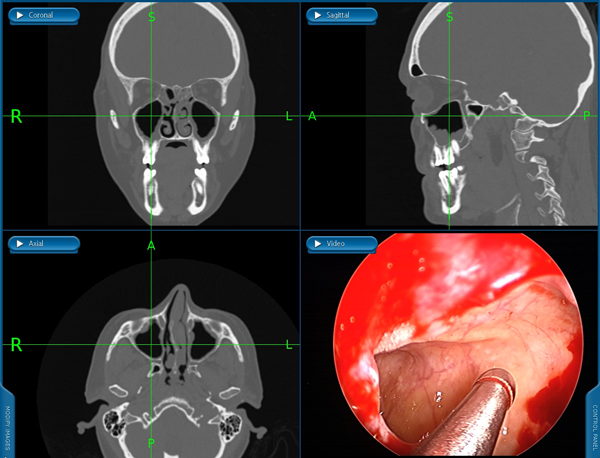 Maxillary Sinus (Cheek Area)
Maxillary Sinus (Cheek Area)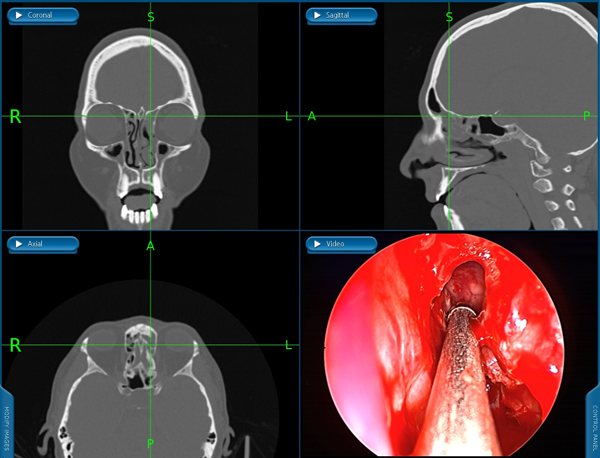 Frontal Sinus (Forehead Area)
Frontal Sinus (Forehead Area)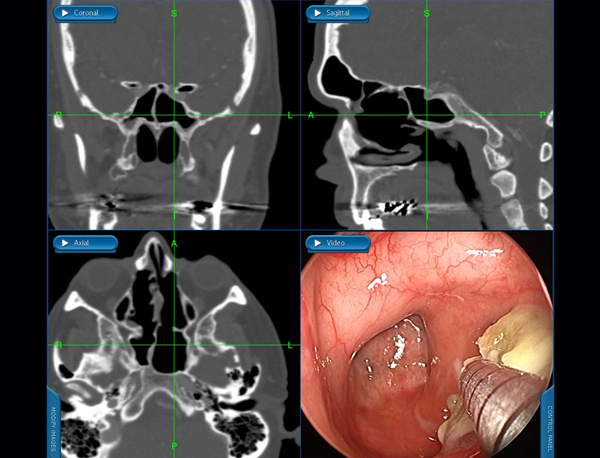 Sphenoid Sinus
Sphenoid SinusEndoscopic Balloon Sinus Dilation (Balloon Sinuplasty)
Endoscopic balloon sinus dilation (balloon sinuplasty) is a very minimally invasive procedure that can be performed in clinic to dilate the natural sinus openings. Balloon dilation of the sinuses can be performed to treat chronic sinusitis and recurrent sinusitis.
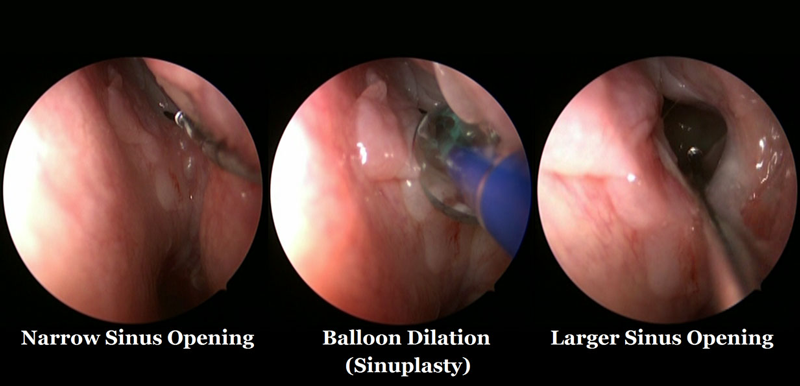
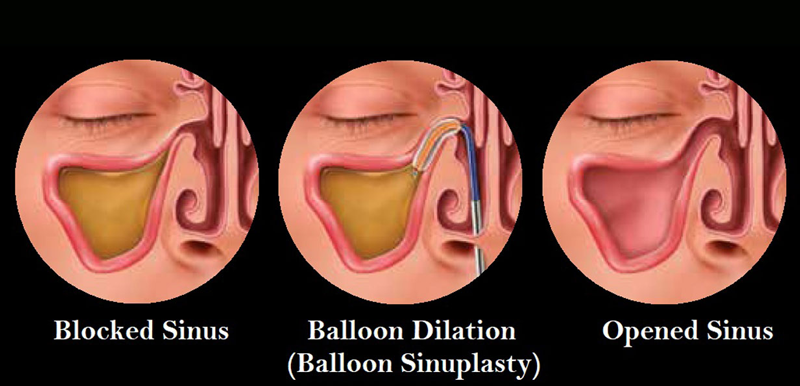
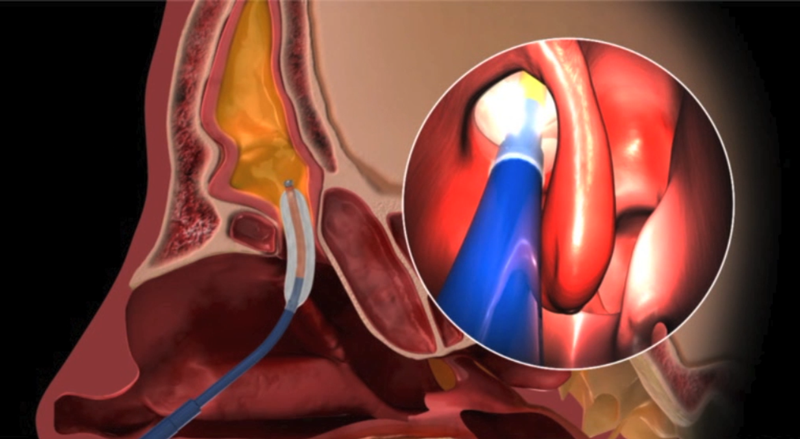 Balloon Sinuplasty
Balloon SinuplastyNasal Endoscopy
Nasal endoscopy is a quick, safe, and painless procedure that evaluates the inside of nose. Nasal endoscopy is performed in a comfortable clinic setting and does not require general anesthesia or sedation of any kind. A tiny endoscope (camera lens) is used to visualize the nasal passages.
Nasal endoscopy is often the first step in diagnosing inflammation of the nose (rhinitis), inflammation of the sinuses (sinusitis), mucous drainage down the throat (post nasal drip), sinus polyps, and sinus masses. Nasal endoscopy also allows for improved evaluation for causes of nasal blockage and nasal obstruction such as a deviated nasal septum and enlarged inferior turbinates (inferior turbinate hypertrophy).
Dr. Flavill has outfitted his clinic with operating room quality equipment and endoscopes. High quality monitors are available in clinic that will allow you to see and understand what is going on inside your nose and sinuses. You will also be able to see the benefits and effectiveness of medications and surgeries in real time during your appointments.
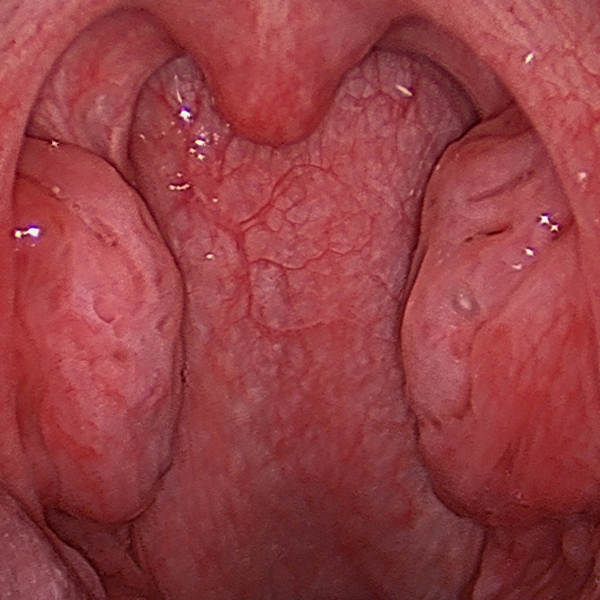
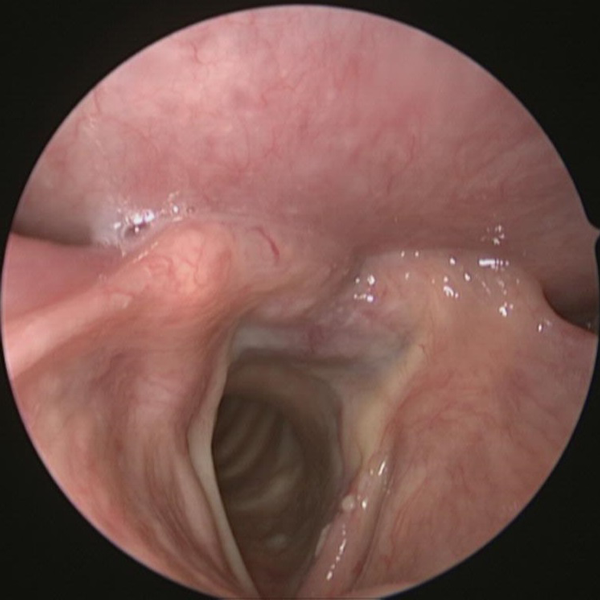
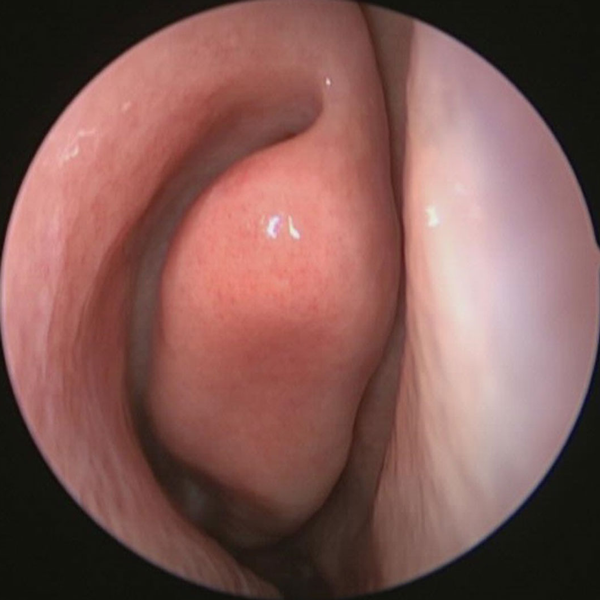 Nasal Endoscopy
Nasal Endoscopy
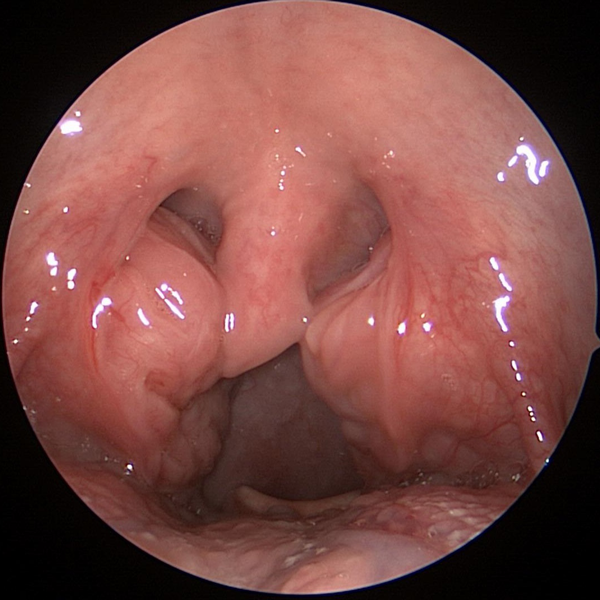
Normal Nasal Endoscopy Showing Middle Turbinate
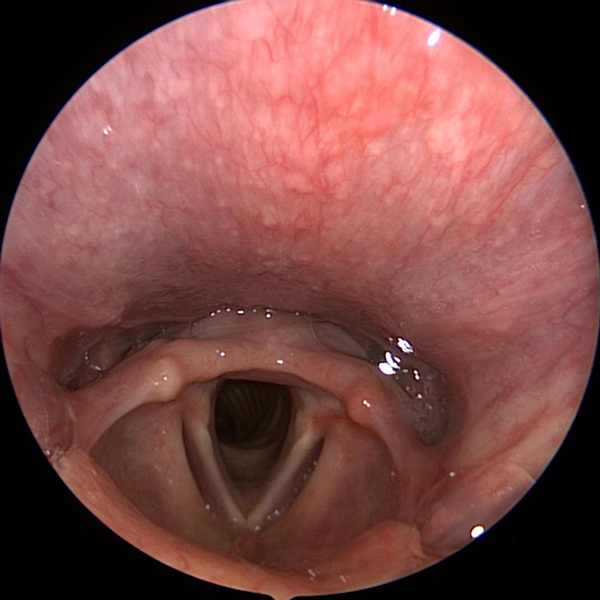
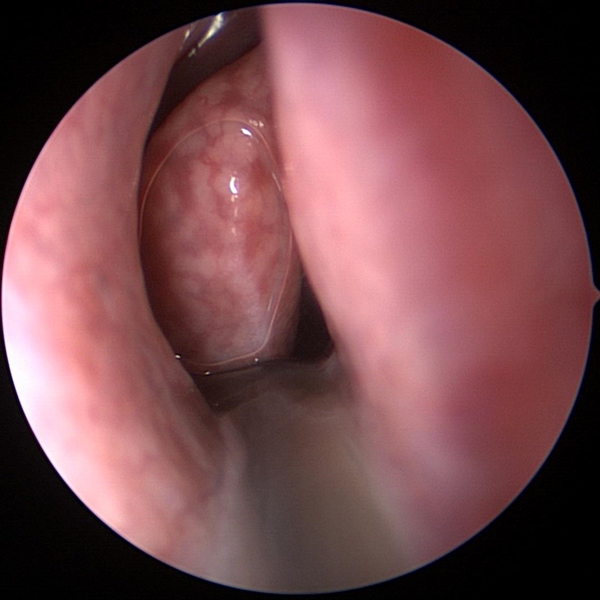 Nasal Endoscopy
Nasal Endoscopy
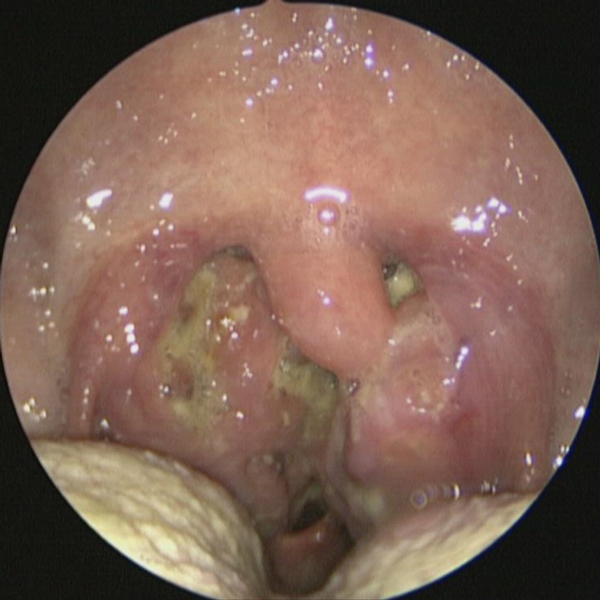
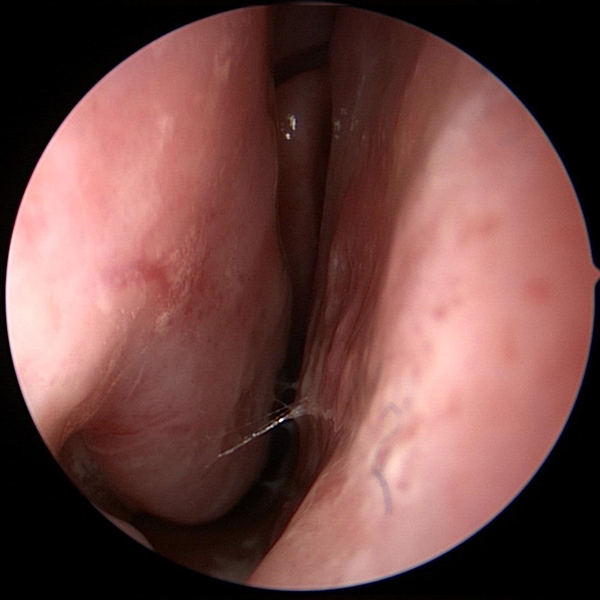
Nasal Endoscopy Showing Abnormal Severe Mucous Collecting In Nose
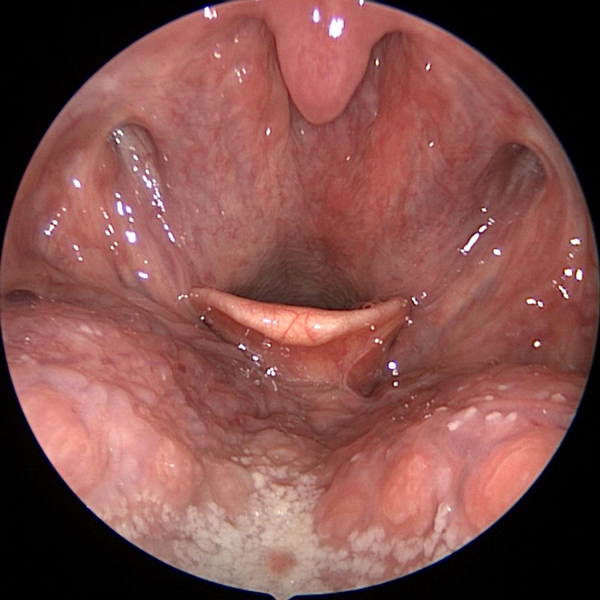
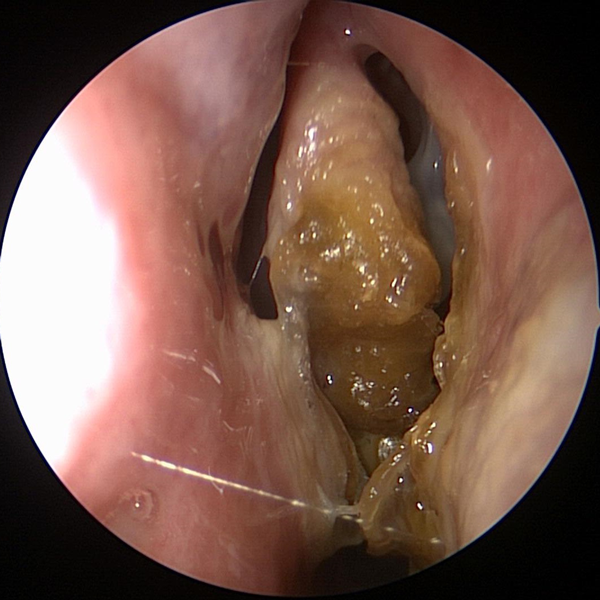 Nasal Endoscopy
Nasal Endoscopy
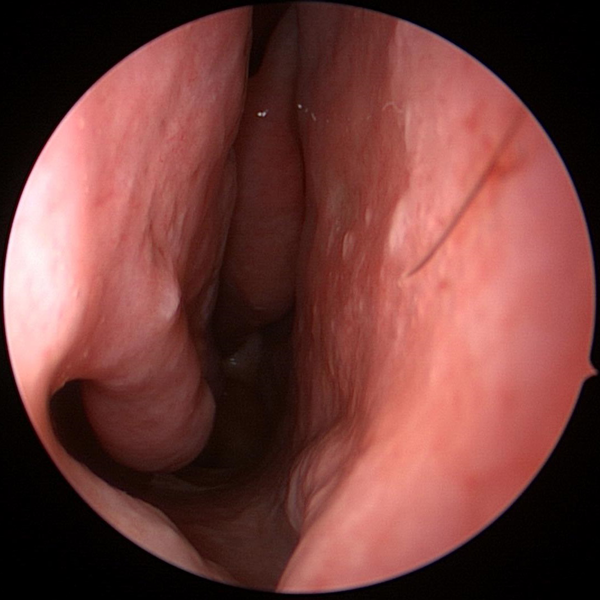
Nasal Endoscopy Showing Crusting & Pus From Chronic Sinusitis
Laryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy allows evaluation of the throat and larynx (voice box). This procedure can be done to evaluate hoarseness, weak voice, throat pain, cough, problems breathing, or swallowing problems.
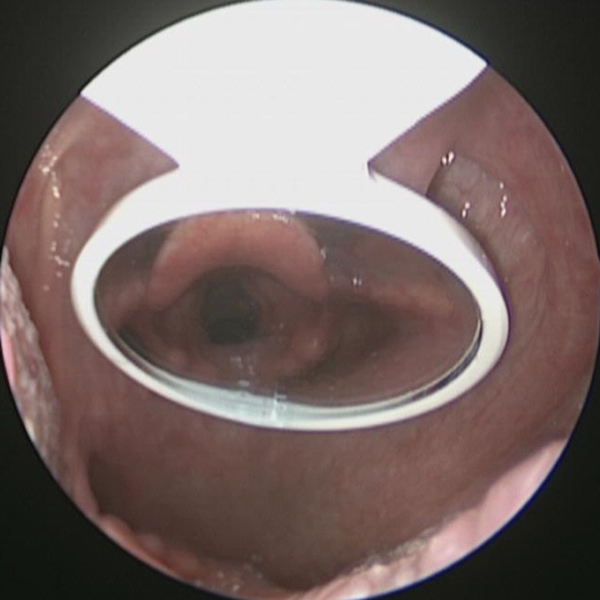 Indirect Laryngoscopy
Indirect Laryngoscopy
Exam with mirror allows some visualization of the larynx (voice box)
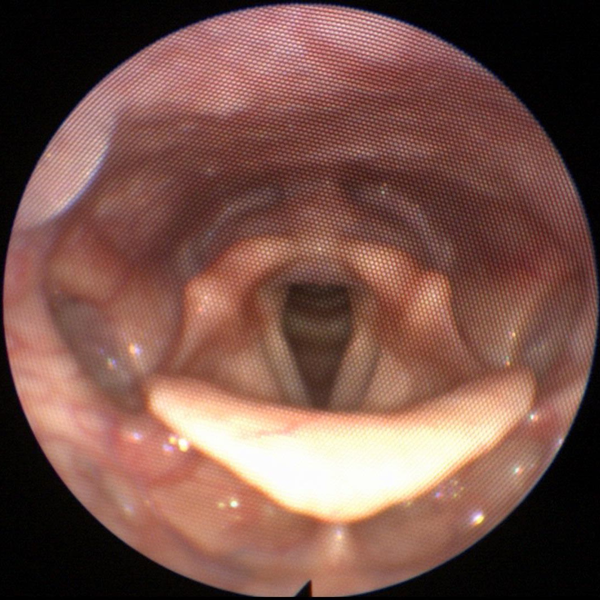 Flexible Fiberoptic Laryngoscopy:
Flexible Fiberoptic Laryngoscopy:
This very low risk, in clinic procedure can be done in just a few minutes and allows evaluation of your throat and larynx (voice box).
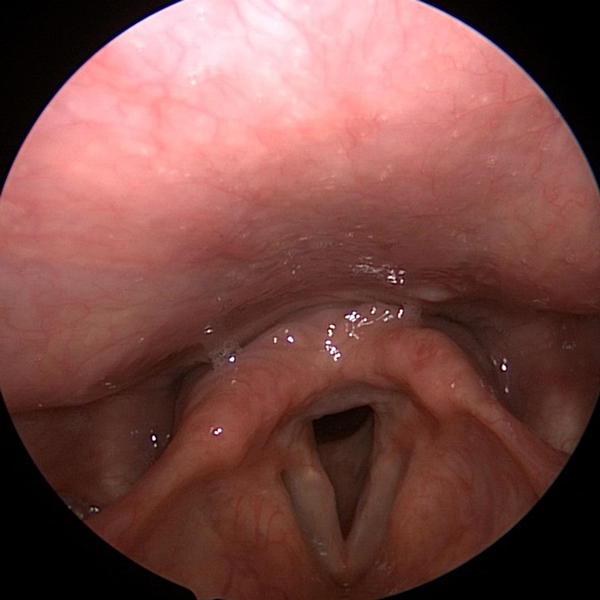 Direct Laryngoscopy
Direct Laryngoscopy
Direct laryngoscopy provides the clearest view of the larynx (voice box)
Septoplasty
This surgery is performed to straighten the nasal septum. The nasal septum is made of bone, cartilage, and soft tissue. If it is crooked or deviated it can cause nasal obstruction and worsened nasal air flow. Septoplasty is performed to correct this.
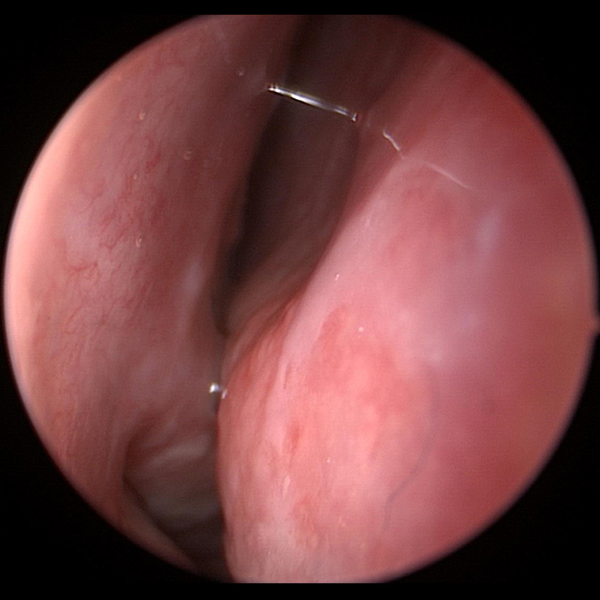 Deviated Nasal Septum
Deviated Nasal Septum
Deviated Septum Before Septoplasty
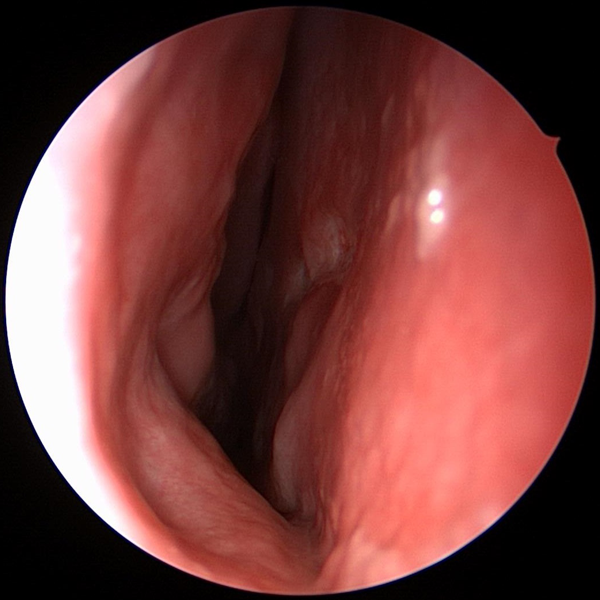 Straight Septum
Straight Septum
Straight Septum After Septoplasty
Septal Perforation Repair
This challenging & intricate surgery is performed to repair holes in the nasal septum. These holes (perforations) can be caused by injury, prior surgeries, or medication use. Septal perforations can cause nasal pain, nasal discomfort, crusting (large boogers), whistling, nose bleeds, & nasal obstruction. Eric Flavill, MD & Jim Gilmore, MD, FACS, FICS researched & developed the Tension Free Septal Perforation Repair Technique (Flavill-Gilmore Procedure) at UT Southwestern Medical Center.
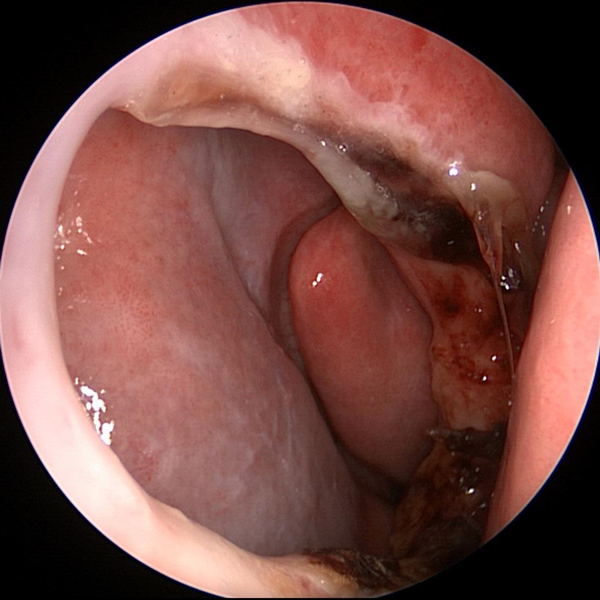 Septal Perforation
Septal Perforation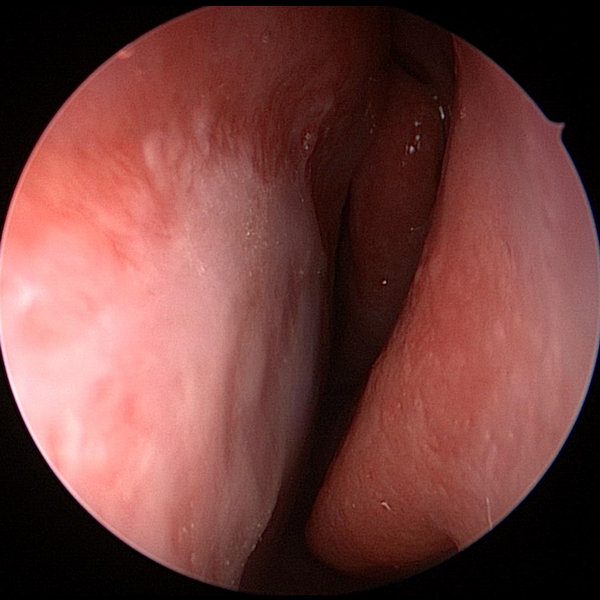 Repaired Septal Perforation
Repaired Septal Perforation
Inferior Turbinate Reduction
The inferior turbinates are made of bone and soft tissue. They are found in your nasal cavity. In some people, the inferior turbinates are very large and can block nasal air flow. This can make nasal breathing difficult. Reducing the size of the inferior turbinates can be a quick and low risk way to relieve nasal obstruction.
 Hypertrophied Inferior Turbinate
Hypertrophied Inferior Turbinate
Large inferior turbinate obstructing airflow at nasal cavity.
 Inferior Turbinate After Reduction
Inferior Turbinate After Reduction
Inferior turbinate after reduction with improved nasal airflow and larger nasal passage.
Treatment Of Nasal Bone Fracture
Nasal bones can be fractured due to trauma & blows to the nose. Fractured nasal bones can cause deformity of the nose & nasal obstruction. Nasal bone fractures can be treated with procedures & surgeries that move these bones back into the normal position.
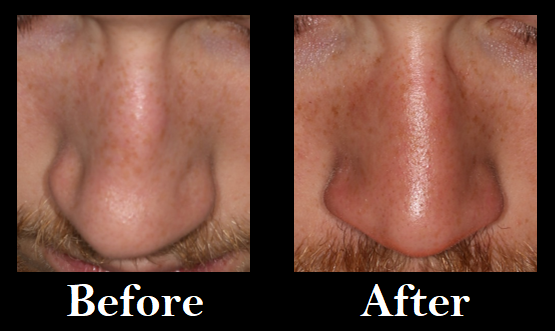 Fractured Nasal Bones Before & After Repair
Fractured Nasal Bones Before & After RepairNasal Reconstruction
Nasal trauma or injury can result in deformity of the nose and nasal obstruction. Surgeries & procedures can be performed to repair & reconstruct the nose.
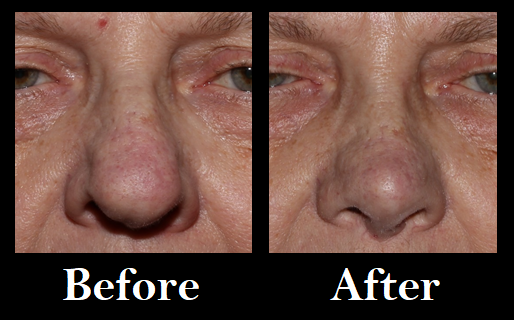 Nasal Reconstruction Before & After Surgery
Nasal Reconstruction Before & After SurgeryTonsillectomy
The palatine tonsil are found at the back of the throat. Tonsillectomy can be done to remove these structures if they are becoming chronically infected or if they are causing other problems due to large size.
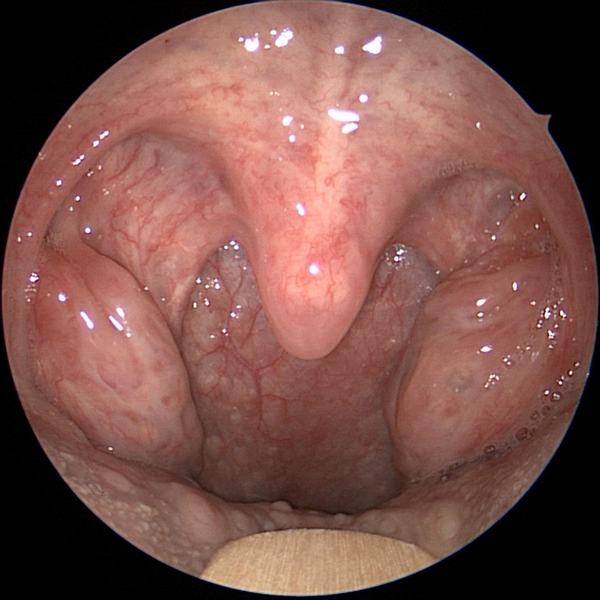 Hypertrophied Tonsils
Hypertrophied Tonsils
Large Tonsils Before Tonsillectomy
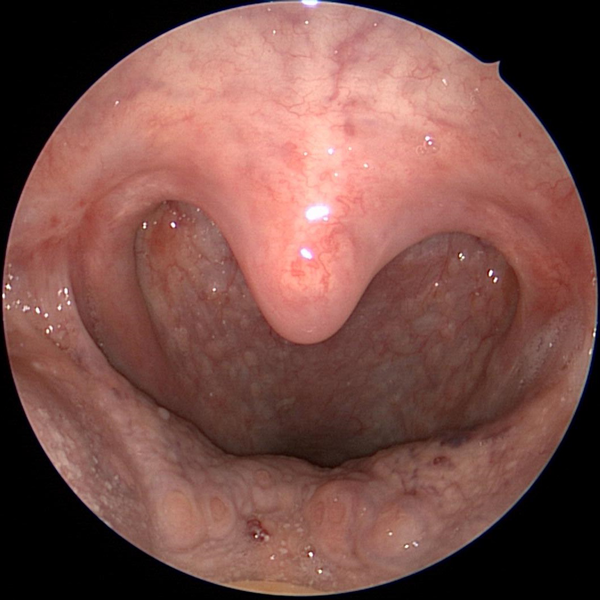 Throat With No Tonsils
Throat With No Tonsils
Throat After Tonsillectomy
Adnoidectomy
The adnoid is a collection of tonsil tissue that exists behind the nose and above the throat. This tissue can become chronically infected or can cause problems due to large size. Adenoidectomy is a surgery to remove or reduce the adnoid tissue.
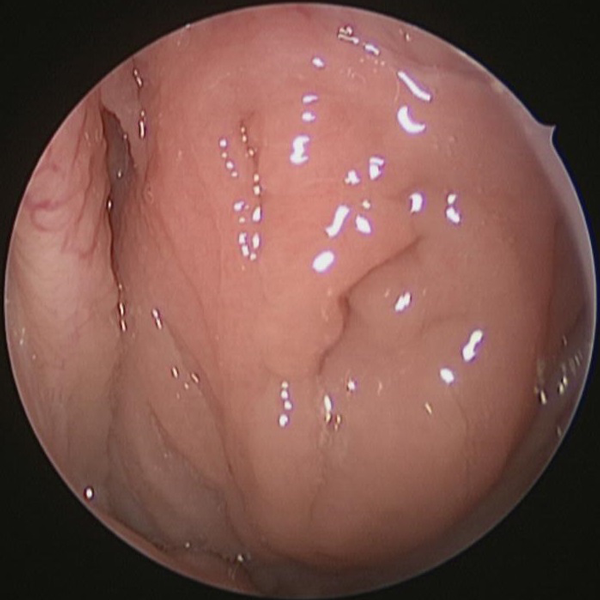 Adenoids Before Adenoidectomy
Adenoids Before Adenoidectomy
Adenoid tissue at nasopharynx (area of throat behind the nose)
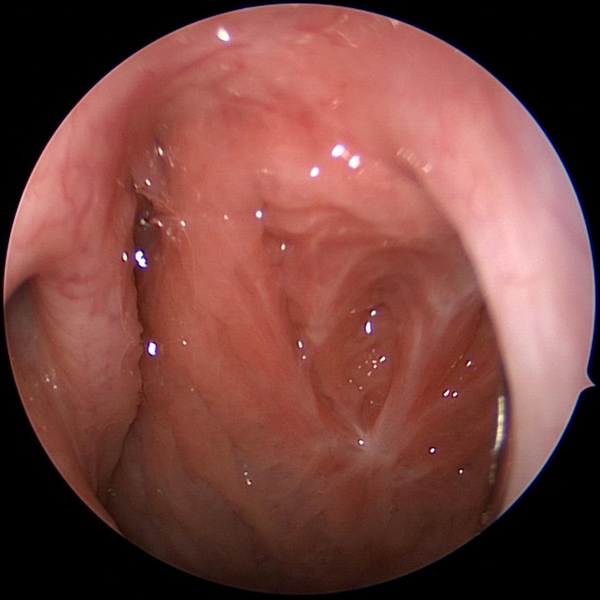 Adenoid Bed After Adenoidectomy
Adenoid Bed After Adenoidectomy
Nasopharynx (area of throat behind the nose) after Adenoidectomy
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UP3)
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty is also known as UP3, UPPP, and Palatopharyngoplasty. This is a surgery done on the throat to help reduce the severity of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Reducing the amount of OSA present can result in better more restful sleep with improved alertness and energy during the day. UP3 can also reduce or resolve snoring symptoms in patients suffering from OSA.
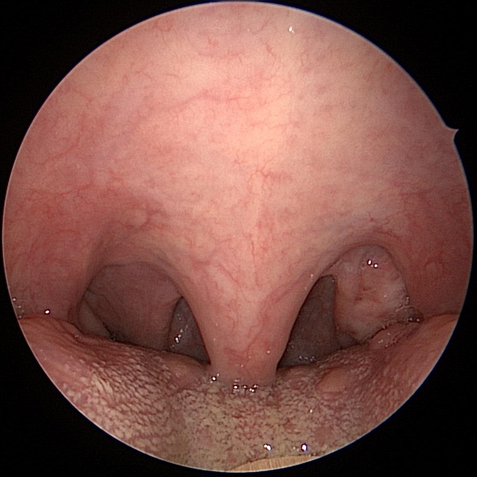 Long Soft Palate With Narrow Throat Airway
Long Soft Palate With Narrow Throat Airway
Throat Before Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UP3)
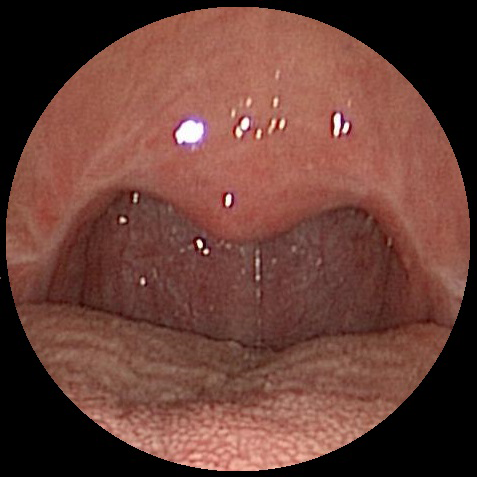 Improved Palate & Throat Airway
Improved Palate & Throat Airway
Throat After Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UP3)
LATERA
Nasal valve collapse is a common cause of nasal obstruction. It results from week lateral cartilage collapsing inward during breathing. LATERA is a self absorbing nasal implant that provides support to the lateral nasal cartilage. It is very minimally invasive & can be placed without external skin incisions.
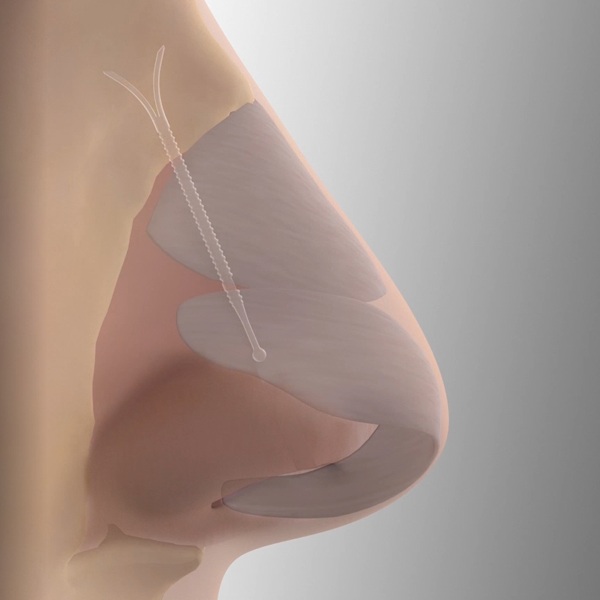 LATERA
LATERA
Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation
Eustachian tube dysfunction can cause ear pain, ear pressure, & even collection of fluid in the middle ear. Eustachian tube balloon dilation is an FDA approved procedure for the treatment of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
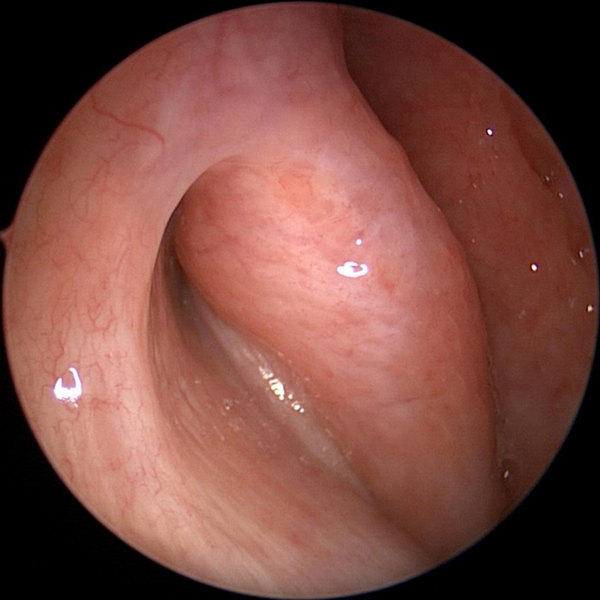 Torus Tubarius Of The Eustachian Tube
Torus Tubarius Of The Eustachian Tube
The torus tubarius are the part of the Eustachian tube that open into the throat
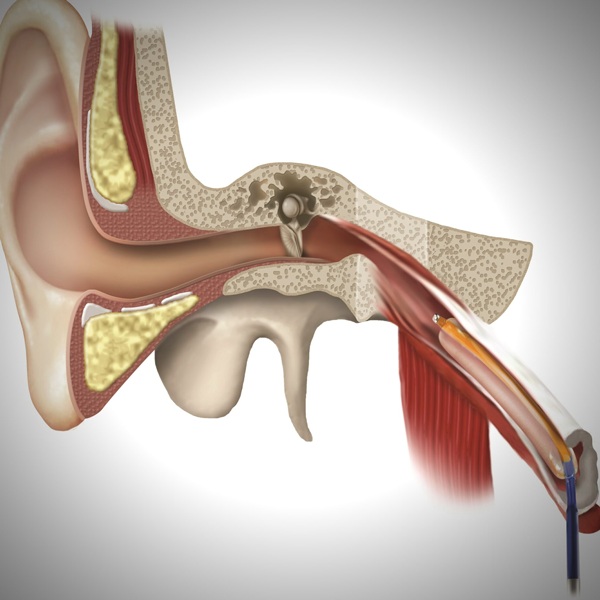 Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation
Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation
The Eustachian tube equalizes pressure in the middle ear by connecting it to the throat.
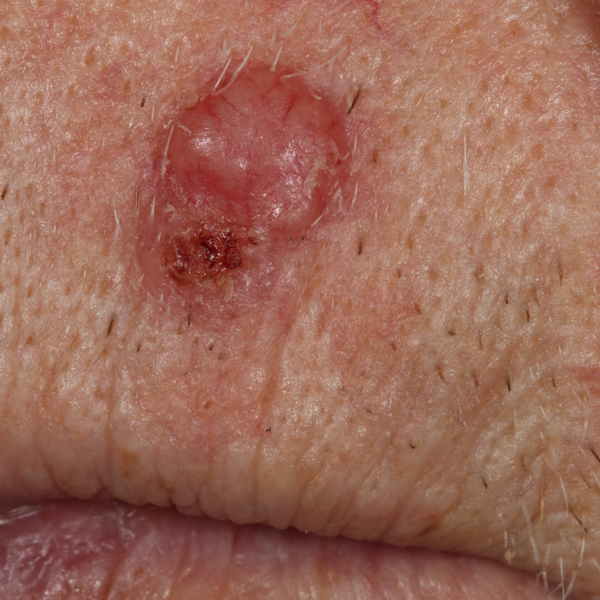
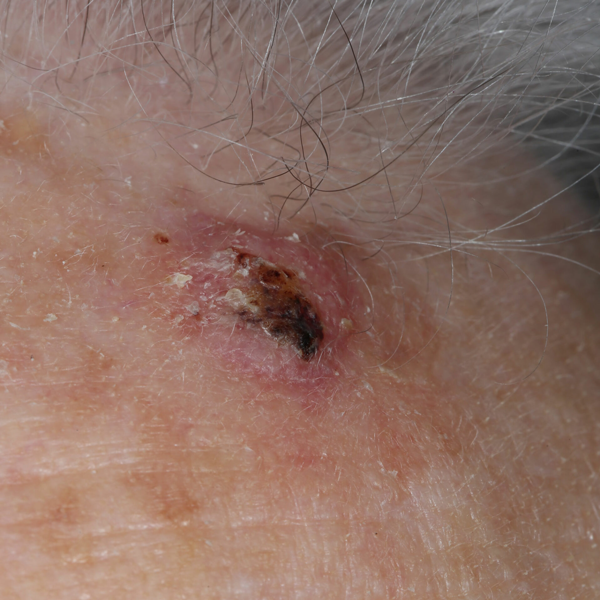
Shave Biopsies
Skin lesions can be evaluated and sometimes removed with this in clinic procedure. The top layers of the skin lesion are shaved off and sent for pathology evaluation.
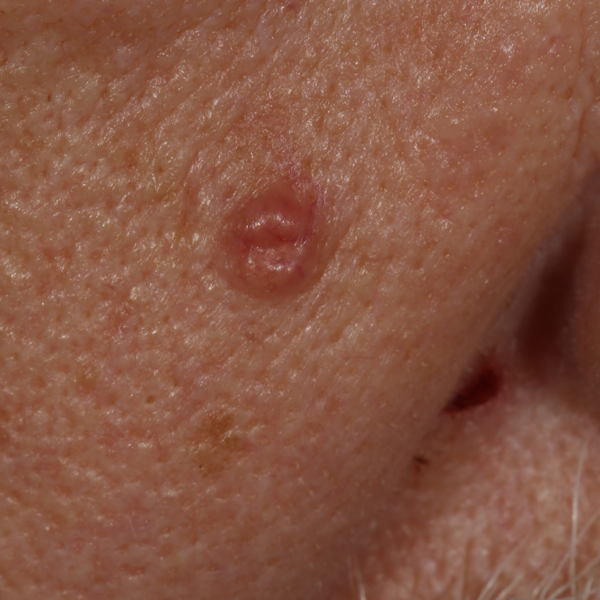 Skin Lesion
Skin Lesion
Skin Neoplasm Before Shave Biopsy
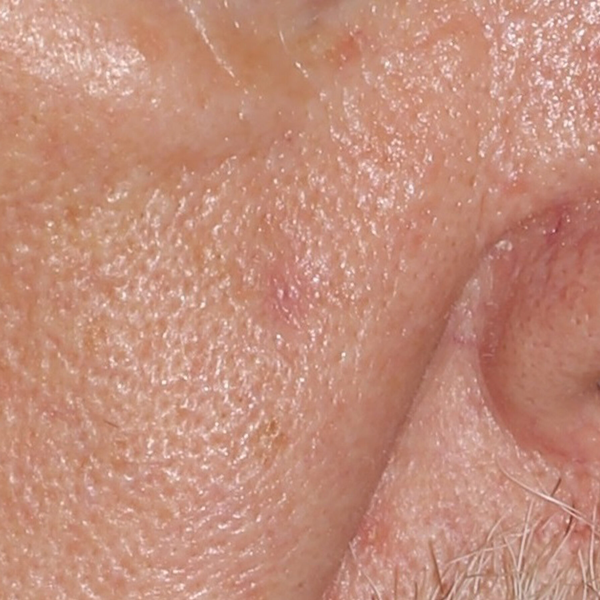 Healed Biopsy Site
Healed Biopsy Site
Healed Skin After Shave Biopsy
Otoendoscopy
Otoendoscopy is an advanced technique for evaluating and treating conditions of the ear. Ear pain (otalgia), ear pressure, ear popping, ear fullness, ear drainage (otorrhea), and sense of hearing loss can all be assessed using otoendoscopy in clinic. A tiny camera is used to examine your ear and obtain images of your ear canal (external auditory canal) and ear drum (tympanic membrane).
Dr. Flavill has outfitted his clinic with operating room quality equipment and top quality optics that will allow you to see and understand what his happening inside your ear. This improved diagnostic information, can help resolve your ear symptoms faster and more effectively.
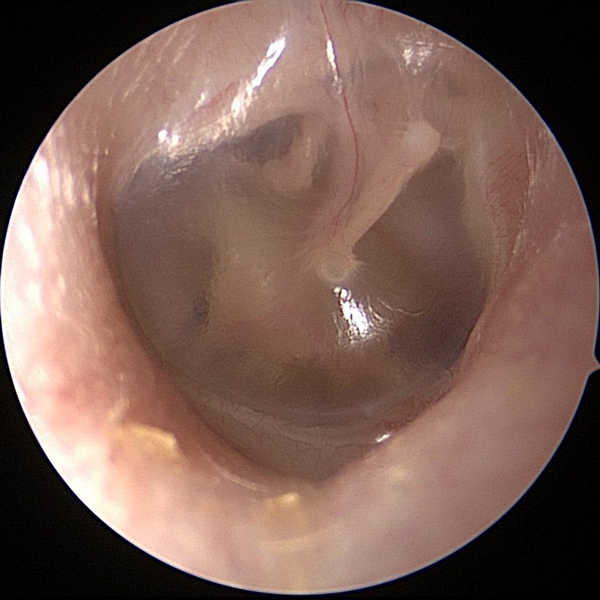 Normal Tympanic Membrane (Ear Drum)
Normal Tympanic Membrane (Ear Drum)
This normal healthy tympanic membrane is translucent (partially see through). The ossicles (tiny ear bones) can be partially visualized.
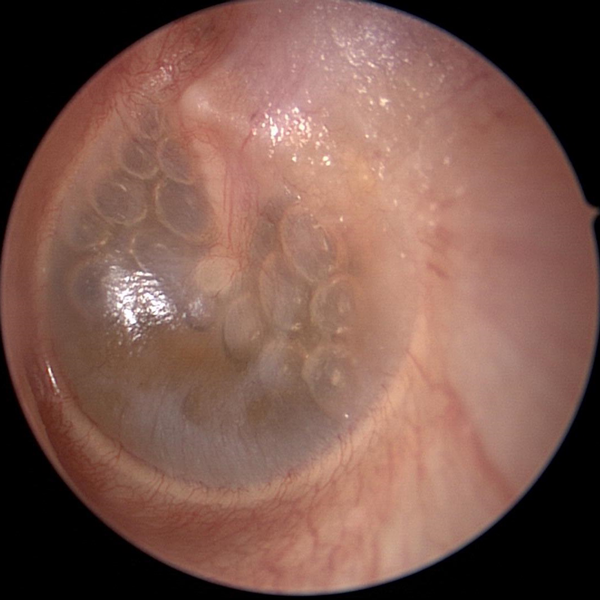 Serous Effusion With Air Bubbles
Serous Effusion With Air Bubbles
Serous effusion (clear sterile fluid) has collected in the middle ear. This fluid is often golden yellow in color. Air bubbles are sometimes seen in the fluid. Swelling or dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can cause this fluid to collect in the middle ear (behind the ear drum).
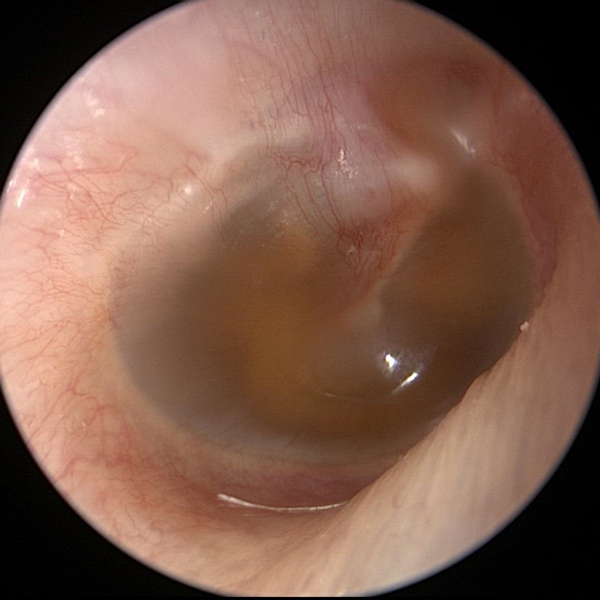 Serous Effusion Without Air Bubbles
Serous Effusion Without Air Bubbles
Serous effusion (clear sterile fluid) has collected in the middle ear. This fluid is often golden yellow in color. Swelling or dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can cause this fluid to collect in the middle ear (behind the ear drum).
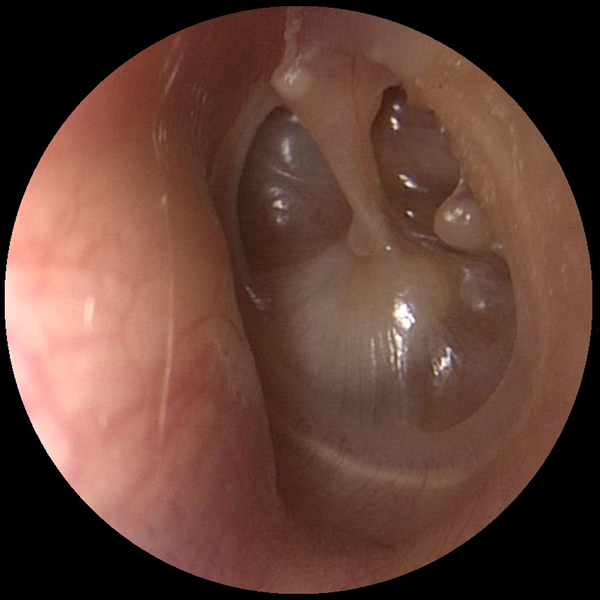 Retracted Tympanic Membrane (Ear Drum)
Retracted Tympanic Membrane (Ear Drum)
Negative pressure can build up in the middle ear due to Eustachian tube dysfunction. This negative pressure can cause the tympanic membrane (ear drum) to retract into the middle ear space.
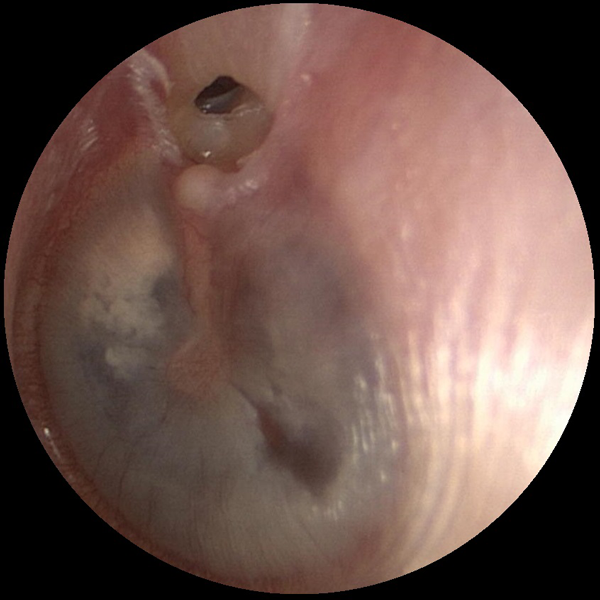 Attic Retraction Pocket
Attic Retraction Pocket
An attic retraction pocket can form in the top part of the tympanic membrane (ear drum) due to negative pressure. Retraction pockets can allow skin cells into the middle ear which can cause an aggressive skin cyst known as cholesteatoma. Otoendoscopy can allow for early detection and treatment.
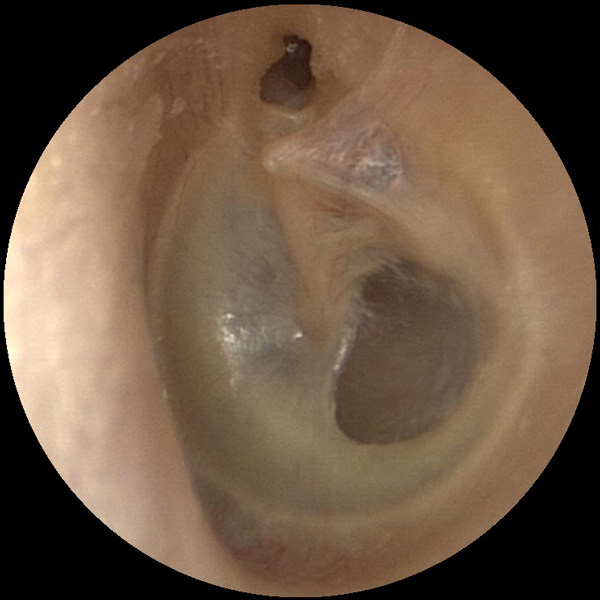 Attic Perforation
Attic Perforation
An attic perforation can form in the top part of the tympanic membrane (ear drum) due to negative pressure. Attic perforations can allow skin cells into the middle ear which can cause an aggressive skin cyst known as cholesteatoma. Otoendoscopy can allow for early detection and treatment.
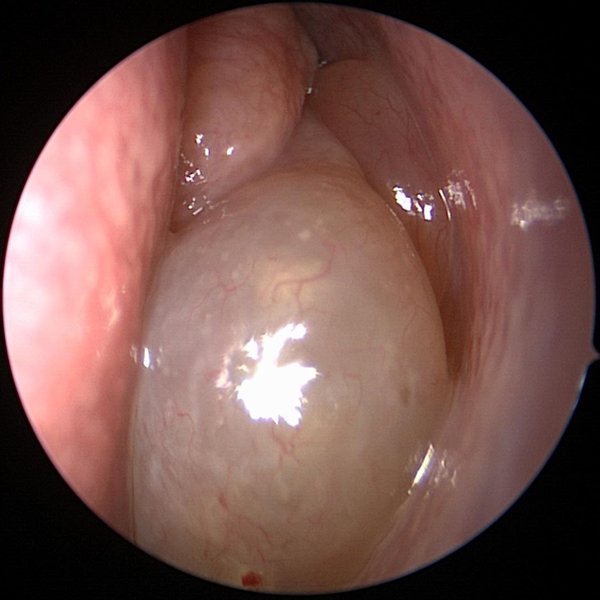
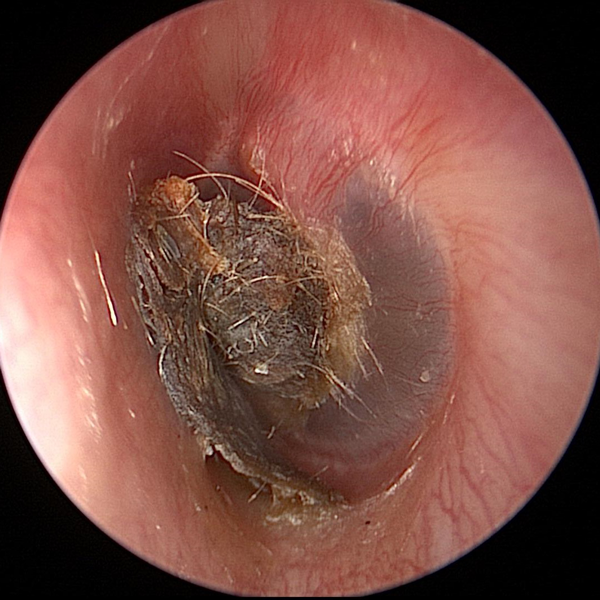 Cerumen (Ear Wax)
Cerumen (Ear Wax)
Cerumen (ear wax) can become impacted against the tympanic membrane (ear drum) due to use of cotton swabs (Q-tips).
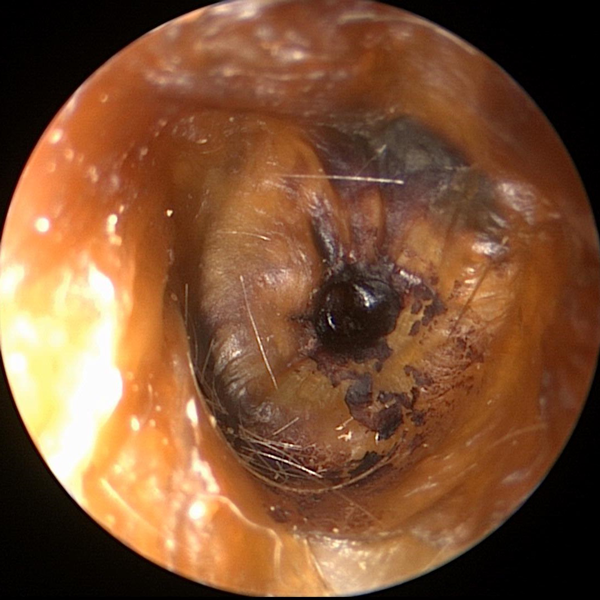 Cerumen (Ear Wax)
Cerumen (Ear Wax)
Cerumen (ear) wax completely coating the tympanic membrane (ear drum).
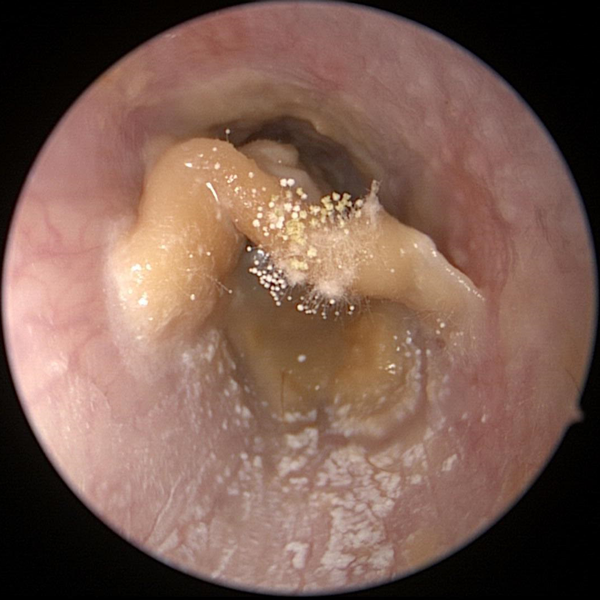 Otomycosis (Fungus)
Otomycosis (Fungus)
Fungus growing on impacted cerumen in the ear canal. Fungus in the ear canal is known as otomycosis
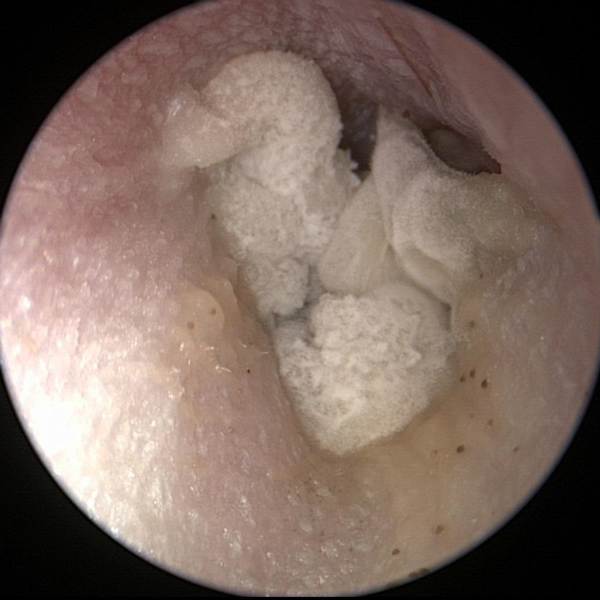 Otomycosis (Fungus)
Otomycosis (Fungus)
Fungal otitis externa (fungal ear infection)
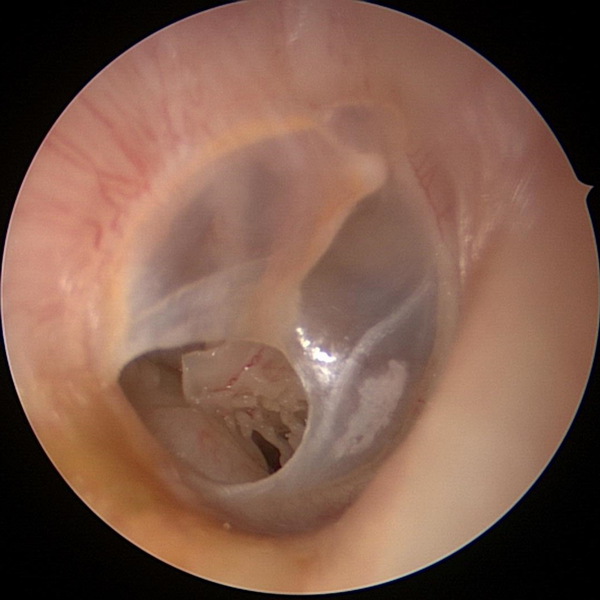 Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Perforation in the tympanic membrane (hole in the ear drum). Middle ear contents
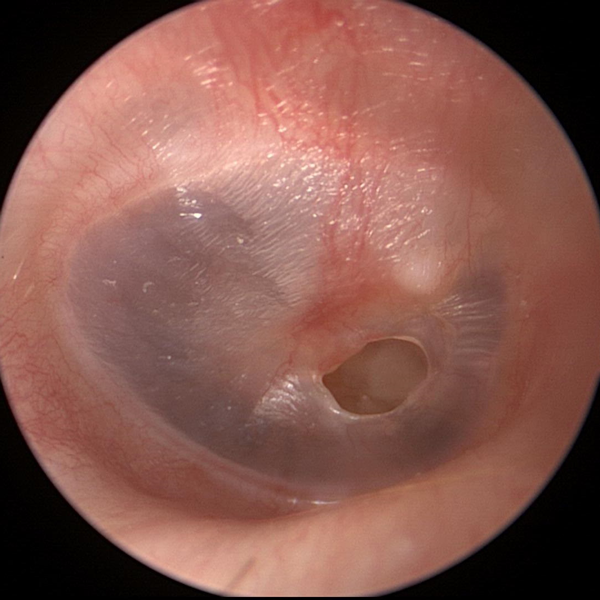 Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Perforation in the tympanic membrane (hole in the ear drum)
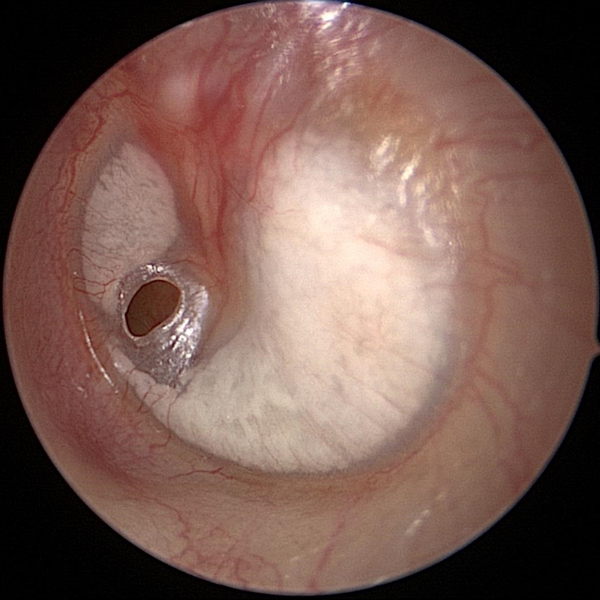 Tympanic Membrane Perforation (Early)
Tympanic Membrane Perforation (Early)
Early tympanic membrane perforation (hole in ear drum). Myringosclerosis (calcifications) are also present.
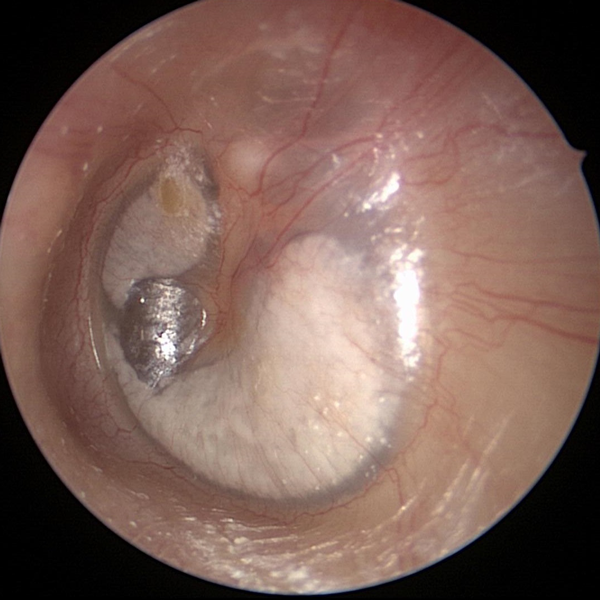 Tympanic Membrane Perforation (Healed)
Tympanic Membrane Perforation (Healed)
Healed tympanic membrane perforation (hole in ear drum). Myringosclerosis (calcifications) are also present.
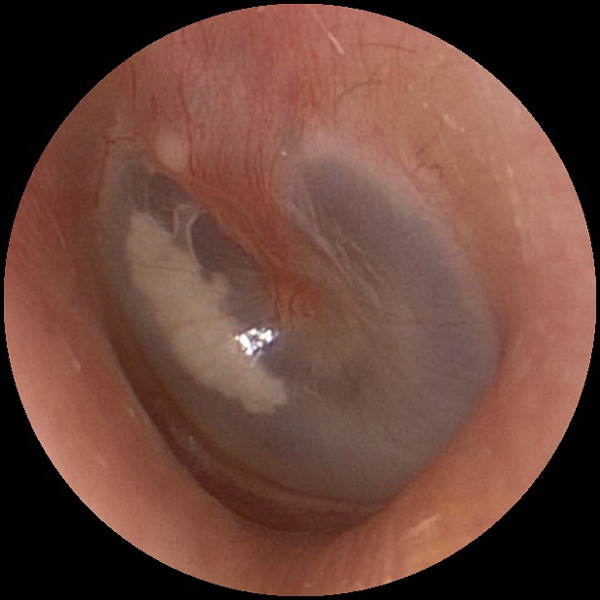 Myringosclerosis (Small)
Myringosclerosis (Small)
Myringosclerosis is a white patch or plaque on the tympanic membrane (ear drum) caused by calcium deposits. Myringosclerosis usually does not effect hearing but can be a sign of past inflammation or infection.
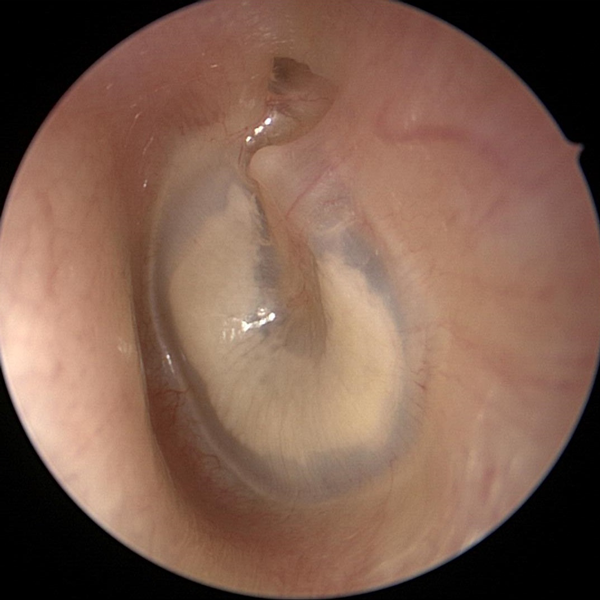 Myringosclerosis (Large)
Myringosclerosis (Large)
Myringosclerosis is a white patch or plaque on the tympanic membrane (ear drum) caused by calcium deposits. Tympanosclerosis is a similar term but is often used to describe calcification that extends into the middle ear space.